ELTD1 promotes gastric cancer proliferation
Sun B & Zhong FJ. ELTD1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Through MAPK/ERK Signaling by Regulating CSK. Int J Gen Med 14:4897-4911 (2021)
How they used Xena
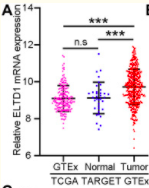
They used data from the TCGA TARGET GTEx cohort to compare tumor vs normal tissues for ELTD1
Paper
Purpose
Patients with gastric cancer (GC) often die from metastasis. However, the exact molecular mechanism underlying GC metastasis is complicated and still remains elusive. Epidermal growth factor, latrophilin and seven-transmembrane domain-containing 1 (ELTD1), has been reported to be involved in cancer metastasis, but its role in GC is still missing.
Patients and methods
We first analyzed the expression of ELTD1 in GC using public databases (TCGA, Oncomine, and GEO) and our clinical samples. The functions of ELTD1 in GC proliferation, invasion and metastasis were determined by in vitro and in vivo experiments. The functional mechanism of ETLD1 in GC was also investigated. Finally, the association between ELTD1 expression and the overall survival of GC patients was analyzed using public databases.
Results
ELTD1 is significantly upregulated in GC tissues. Knockdown of ELTD1 inhibits GC cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro as well as tumor growth and metastasis in vivo, while ELTD1 overexpression obtains opposite results. Moreover, ELTD1 could promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in GC. Mechanistically, ELTD1 exerts its tumor-promoting effect by activating MAPK/ERK signaling. Subsequent studies demonstrated that ELTD1 could interact with C-terminal Src kinase (CSK) and inhibit its expression, which finally lead to MAPK/ERK activation. Data from TGCA and GEO both revealed that GC patients with high ELTD1 expression had poorer prognosis and the combination of ELTD1 with CSK showed better predictive performance.
Conclusion
ELTD1 plays an oncogene role in GC through MAPK/ERK signaling via inhibiting CSK, which may be a useful prognostic predictor and potential therapeutic target for GC.