Increased expression of KPNA2 predicts unfavorable prognosis in ovarian cancer patients
Cui X, Wang H, Wu X, Huo K & Jing X. Increased expression of KPNA2 predicts unfavorable prognosis in ovarian cancer patients, possibly by targeting KIF4A signaling. Journal of Ovarian Research (2021)
How they used Xena
They used Xena to make Figure 1 and to help make Figure 6, where they explored the correlation between KPNA2 and KIF4A mRNA expression
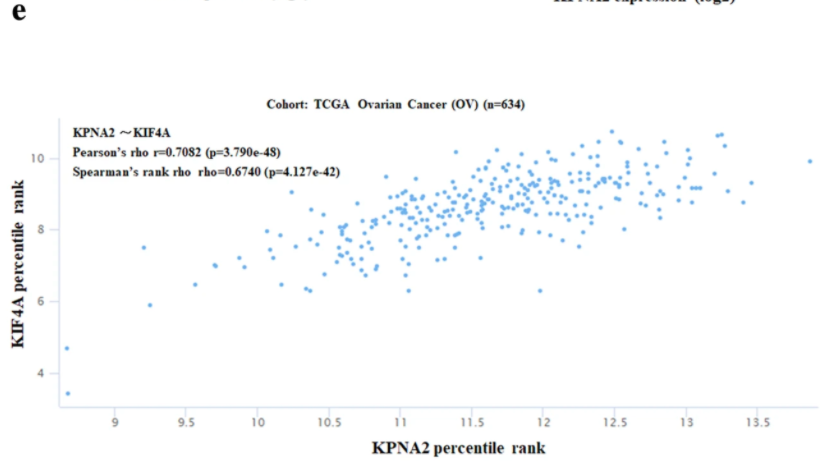
Figure 6 from the paper
Join the conversation on Twitter about this publication
Paper
Background
Karyopherin α-2 (KPNA2) is a member of karyopherin family, which is proved to be responsible for the import or export of cargo proteins. Studies have determined that KPNA2 is associated with the development and prognosis of various cancers, yet the role of KPNA2 in ovarian carcinoma and its potential molecular mechanisms remains unclear.
Materials and methods
The expression and prognosis of KPNA2 in ovarian cancer was investigated using GEPIA and Oncomine analyses. Mutations of KPNA2 in ovarian cancer were analyzed by cBioPortal database. The prognostic value of KPNA2 expression was evaluated by our own ovarian carcinoma samples using RT-qPCR. Subsequently, the cell growth, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells were investigated by CCK-8 and transwell assay, respectively. The protein levels of KPNA2 and KIF4A were determined by western blot.
Results
We obtained the following important results. (1) KPNA2 and KIF4A wereoverexpressed in ovairan cancer tissues and cells. (2) Among patients with ovarian cancer, overexpressed KPNA2 was associated with lower survival rate. (3) Mutations (R197* and S140F) in KPNA2 will have some influences on protein structure, and then may cause protein function abnormal. (4) KPNA2 konckdown inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, as well as the expression of KIF4A.
Conclusion
KPNA2, as a tumorigenic gene in ovarian cancer, accelerated tumor progression by up-regulating KIF4A, suggesting that KPNA2 might be a hopeful indicator of treatment and poor prognosis.